The Litter Olympics: Addressing Individual Critical Tasks Lists Requirements in a Forward-Deployed Setting
Background: Individual critical tasks (ICTs) specify the skills and knowledge required for each military occupational specialty (MOS) for enlisted soldiers and areas of concentration (AOCs) for officers. This article describes a structured training method designed to enhance ICT proficiency and reinforce other critical medical skills while deployed in a Role 3 environment in Baghdad, Iraq. The Litter Olympics approach integrates interdisciplinary collaboration and physical exertion into skill reinforcement to improve medical readiness.
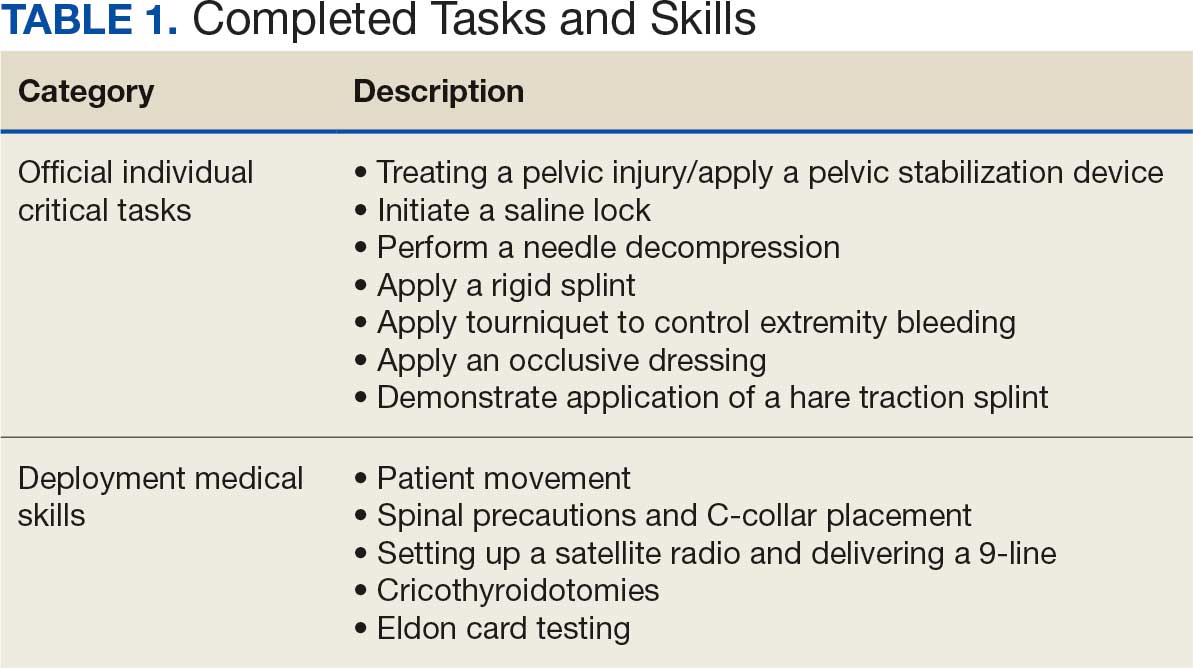
Observations: The Litter Olympics were conducted with mixed MOS/AOC teams, including nonmedical personnel such as administrative, signal, and engineering specialists. Teams progressed through a series of stations inside and outside the Role 3 hospital, completing ICTs under the supervision of higher-level health care practitioners. Tasks were selected based on their relevance to deployed medical care and their inclusion in ICTs, ensuring alignment with mission-essential skills. Participants completed essential ICTs, including initiating saline locks, applying occlusive dressings, performing needle decompressions, applying tourniquets, and treating pelvic injuries with stabilization devices. Additional deployment-relevant skills included patient movement inside and outside a hospital setting, maintaining spinal precautions, establishing communication via satellite radio, executing a 9-line MEDEVAC request, performing cricothyroidotomies, and conducting Eldon card testing. All teams completed the course within 2 hours and feedback suggested increased confidence and proficiency in critical skills.
Conclusions: The Litter Olympics provide a structured, reproducible format for sustaining medical readiness in a deployed Role 3 setting. By integrating interdisciplinary teamwork, physical engagement, and practical skill application, it offers a dynamic alternative to traditional training methods. This model can be adapted for both deployed and stateside training environments, enhancing medical preparedness while fostering esprit de corps.
Military medical personnel rely on individual critical tasks lists (ICTLs) to maintain proficiency in essential medical skills during deployments. However, sustaining these competencies in a low-casualty operational setting presents unique challenges. Traditional training methods, such as lectures or simulations outside operational contexts, may lack engagement and fail to replicate the stressors of real-world scenarios. Previous research has emphasized the importance of continuous medical readiness training in austere environments, highlighting the need for innovative approaches.1,2
The Litter Olympics was developed as an in-theater training exercise designed to enhance medical readiness, foster interdisciplinary teamwork, and incorporate physical exertion into skill maintenance. By requiring teams to carry a patient litter through multiple “events,” the exercise reinforced teamwork within a medical readiness-focused series inspired by an Olympic decathlon. This article discusses the feasibility, effectiveness, and potential impact of the Litter Olympics as a training tool for maintaining ICTLs in a deployed environment.
Program
The Litter Olympics were implemented at a Role 3 medical facility in Baghdad, Iraq, where teams composed of individuals from military occupational specialties (MOSs) and areas of concentration (AOCs) participated. Role 3 facilities provide specialty surgical and critical care capabilities, enabling a robust medical training environment.3 The event was designed to reflect the interdisciplinary nature of deployed medical teams and incorporated hands-on training stations covering critical medical skills such as traction splinting, spinal precautions, patient movement, hemorrhage control, airway management, and tactical evacuation procedures.
Tasks were selected based on their relevance to deployed medical care and their inclusion in ICTLs, ensuring alignment with mission-essential skills. Participants were evaluated on task completion, efficiency, and teamwork by experienced medical personnel. Postexercise surveys assessed skill improvement, confidence levels, and areas for refinement. Future studies should incorporate structured performance metrics, such as pre- and postevent evaluations, to quantify proficiency gains (Table 1).
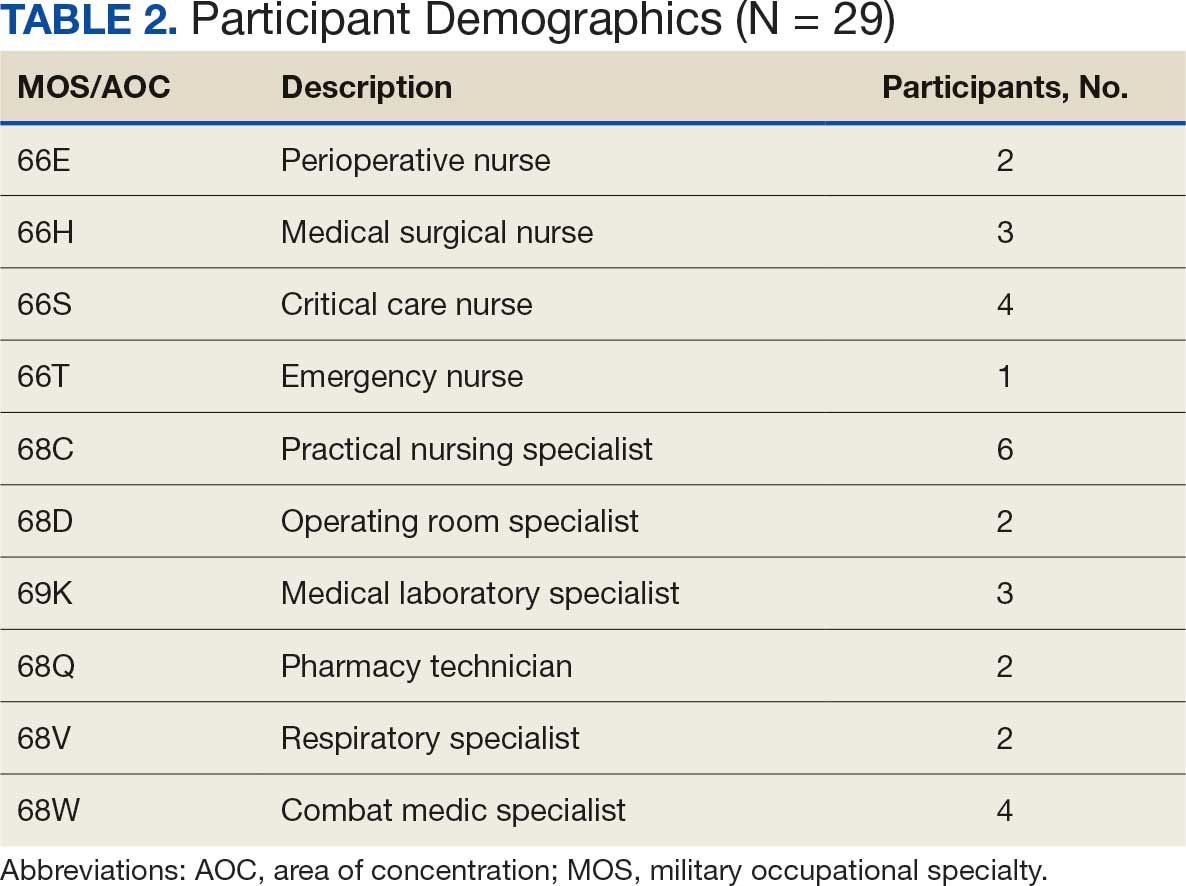
Five mixed MOS/AOC teams participated in the event, completing the exercise in an average time of 50 minutes (Table 2). Participants reported increased confidence in performing ICTs, particularly in patient movement, hemorrhage control, and airway management. The interdisciplinary nature of the teams facilitated peer teaching and cross-training, allowing individuals to better understand each other’s roles and responsibilities. This mirrors findings in previous studies on predeployment training that emphasize the importance of collaborative, hands-on learning.4 The physical aspect of the exercise was well received, as it simulated operational conditions and reinforced endurance in high-stress environments. Some tasks, such as cricothyroidotomy and satellite radio setup, required additional instruction, highlighting areas for improvement in future iterations.
Discussion
The Litter Olympics provide a dynamic alternative to traditional classroom instruction by integrating realistic, scenario-based training. However, several limitations were identified. The most significant was the lack of formalized outcome metrics. While qualitative feedback was overwhelmingly positive, no structured performance assessment tool, such as pre- and postevent skill evaluations, was used. Future studies should incorporate objective measures of competency to strengthen the evidence base for this training model. Additionally, participant feedback suggested that more structured debriefing sessions postexercise would enhance learning retention and provide actionable insights for future program modifications.
Another consideration is the scalability and adaptability of the exercise. While effective in a Role 3 setting, modifications may be required for smaller units or lower levels of care. Future iterations could adapt the format for Role 1 or 2 environments by reducing the number of stations while preserving the core training elements. Furthermore, the event relied on access to specialized personnel and equipment, which may not always be feasible in austere settings. Developing a streamlined version focusing on essential tasks could improve accessibility and sustainability across different operational environments.
Participants expressed a preference for this hands-on, competitive training model over traditional didactic instruction. However, further research should compare skill retention rates between the Litter Olympics and other training modalities to validate effectiveness. While peer teaching was a notable strength of the event, structured mentorship from senior medical personnel could further enhance skill acquisition and reinforce best practices.
Conclusions
The Litter Olympics present a reproducible, engaging, and effective method for sustaining medical readiness in a deployed Role 3 setting. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and incorporating physical and cognitive stressors, it enhances both individual and team preparedness. Future research should develop standardized, measurable outcome assessments, explore application in diverse deployment settings, and optimize scalability for broader military medical training programs. Standardized evaluation tools should be developed to quantify performance improvements, and the training model should be expanded to include lower levels of care and nonmedical personnel. Structured debriefing sessions would also provide valuable insight into lessons learned and potential refinements. By integrating these enhancements, the Litter Olympics can serve as a cornerstone for maintaining operational medical readiness in deployed environments.




