Data Trends 2025: Neurology





Reviewed by: Carl Robinson, MD, Chief of Neurology, Togus VA Medical Center, Augusta, Maine
Dr. Robinson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.





Active-duty military personnel and veterans experience unique neurologic morbidity compared to the general population.1 Over 500,000 service members have been diagnosed with TBI from 2000-2024.2 Many of these veterans have mental and physical health comorbidities, and up to 84% higher risk of all-cause mortality.3,4 TBI is associated with other neurological conditions, such as posttraumatic headaches, migraines, and epilepsy.5,6 In a large cohort study, migraine prevalence was found to be approximately 10%, with prevalence as high as 30% in women veterans.5 Migraine and TBI co-occur in 2.3% of veterans, exacerbating cognitive dysfunction more than either condition alone.7 Veterans with multiple sclerosis (MS) face higher risks of dementia, depression, and cannabis use disorder, with mental health risks being amplified by younger age, minority status, combat exposure, and disability.8,9
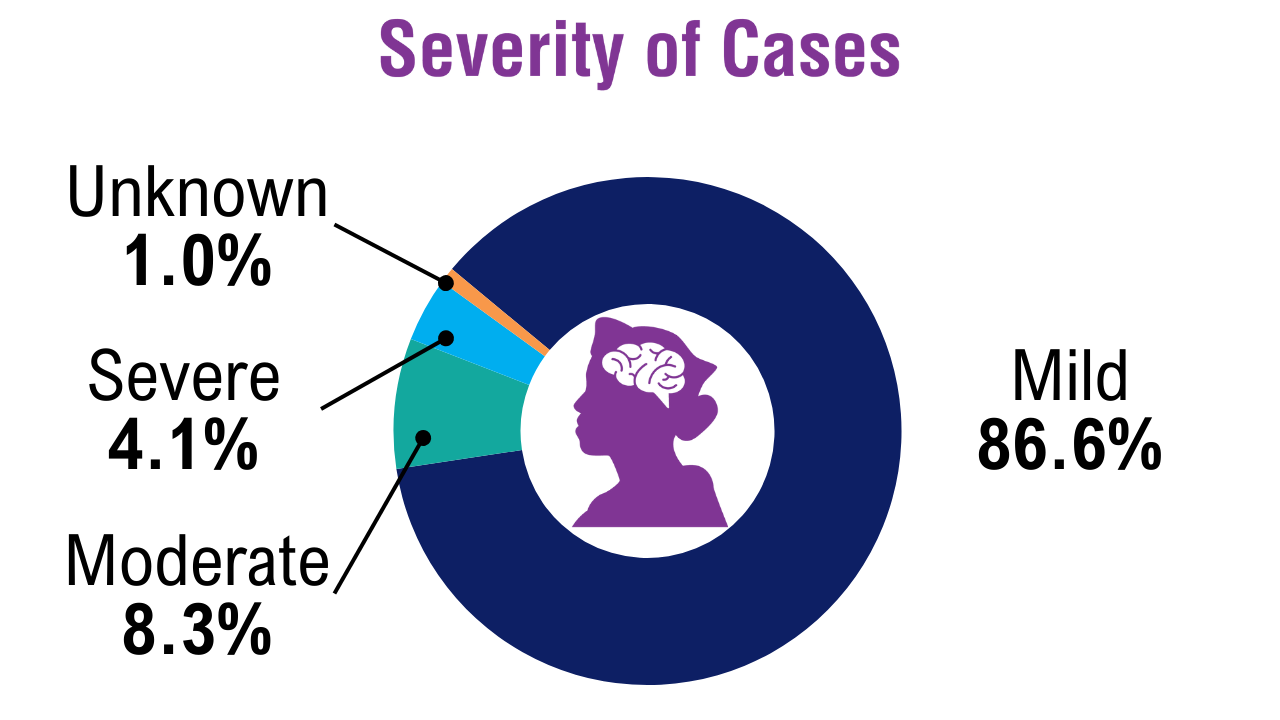 TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
The VA TBI Health Registry includes 441,639 veterans with TBI symptoms who sought care from September 2001 to September 2021.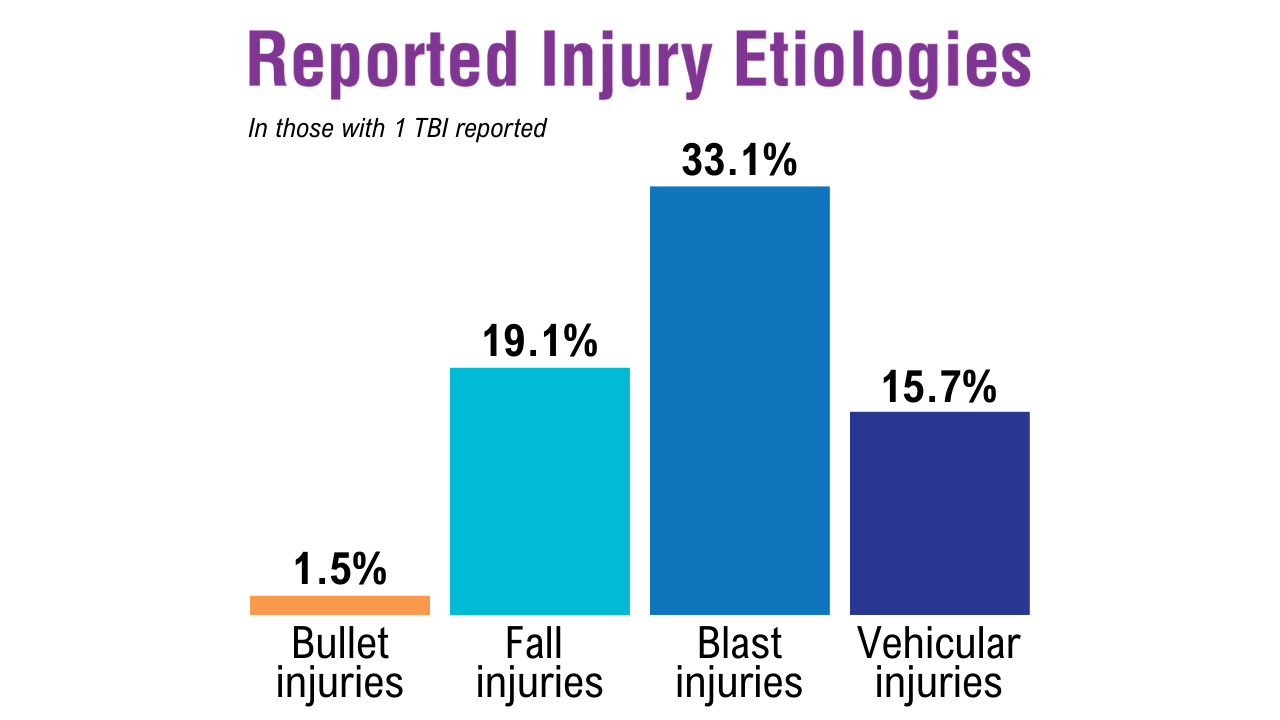 TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
This cohort represents 28.5% of all post-9/11 veterans who sought care at the VHA over a 2-decade period.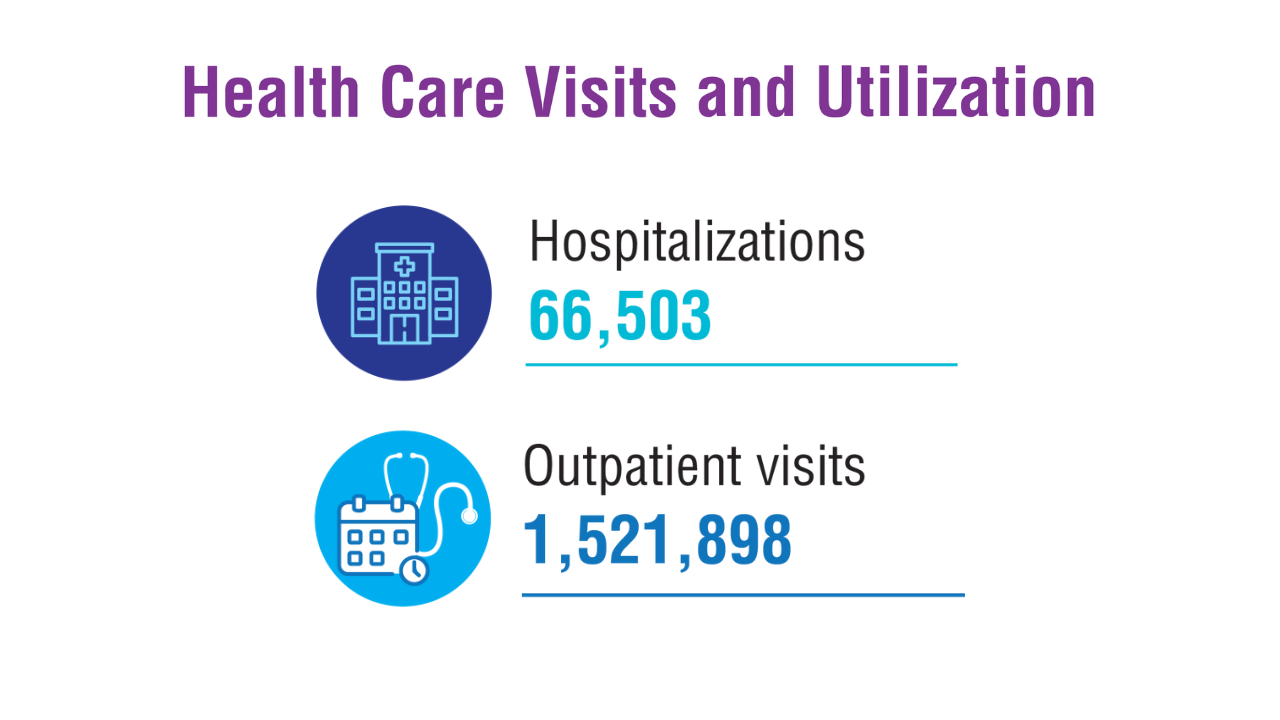 TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
Veterans with TBI accounted for 11.0% of all inpatient care and 12.1% of all outpatient visits at the VHA. More than 108,000 veterans from this group submitted TBI-related disability claims.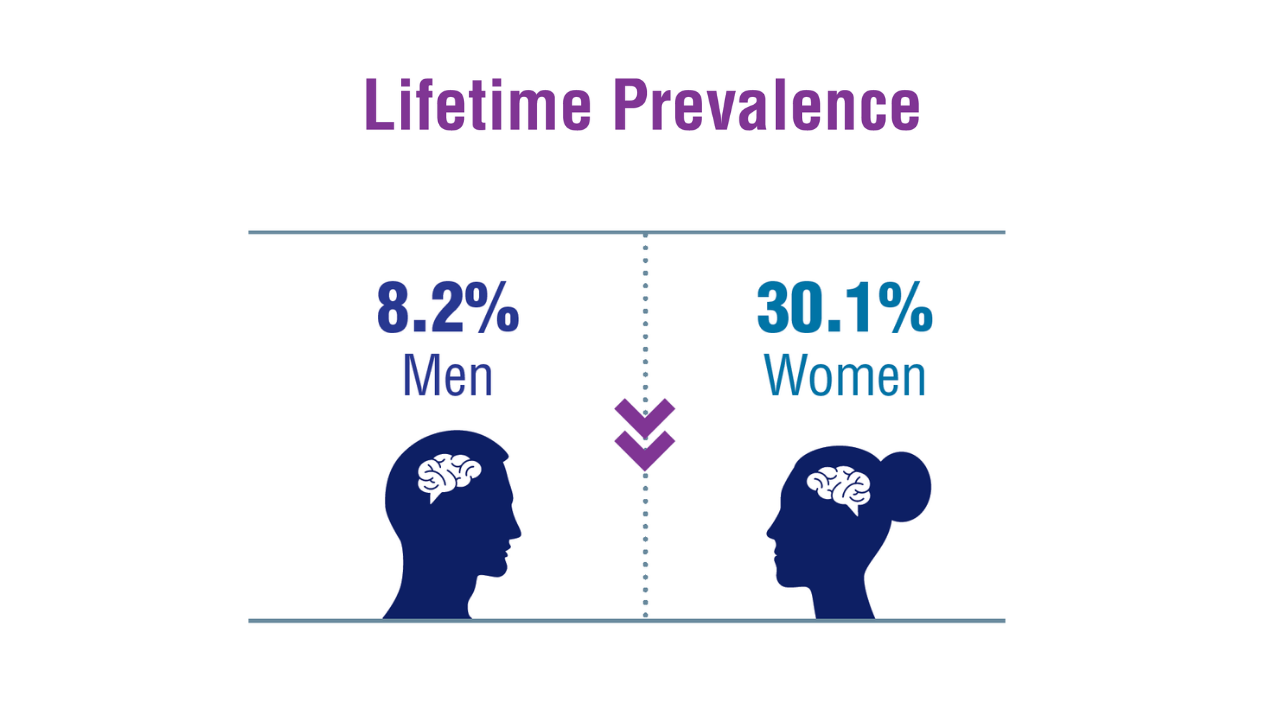 Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
A study of 491,604 veterans analyzed data from the Million Veteran Program to assess the prevalence of migraine and the effect of comorbidities and military service exposures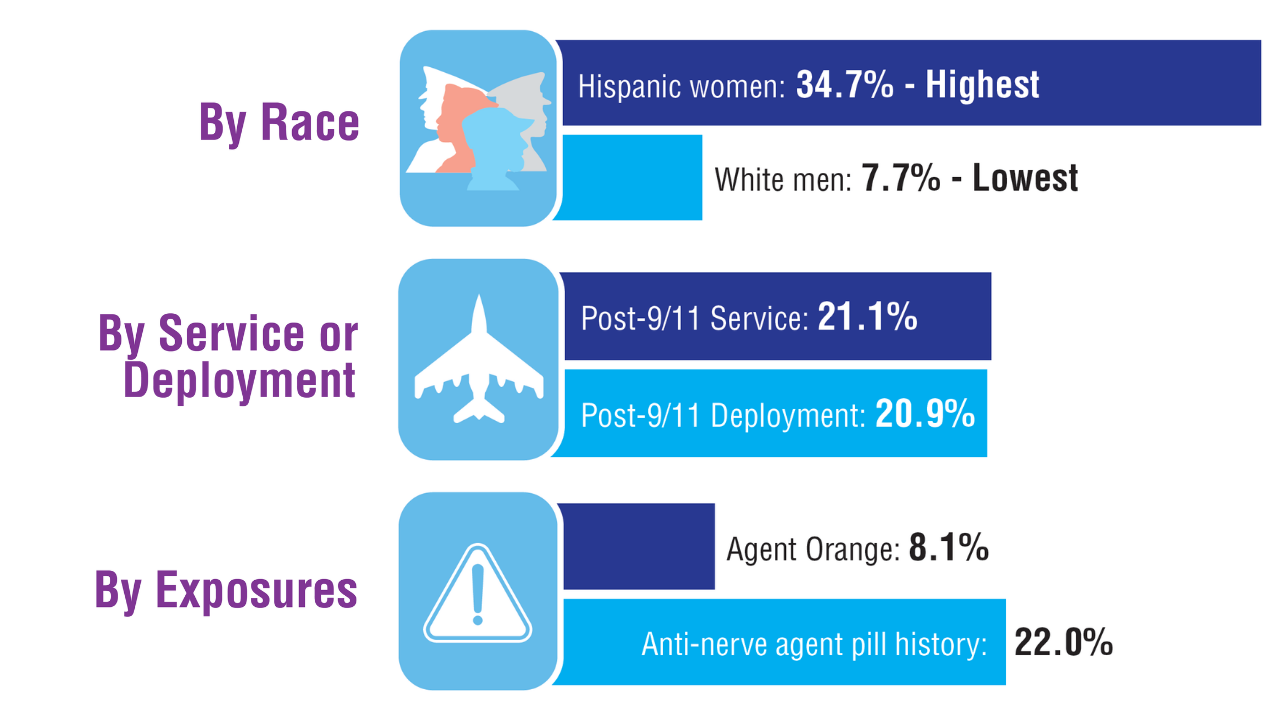 Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
Veterans with migraine were younger (by 8.7 years on average), less likely to be married or cohabiting, and less likely to have a household income < $60,000 than veterans without migraine. Migraine was also associated with TBI, with an odds ratio of 4.82 in men and 2.92 in women.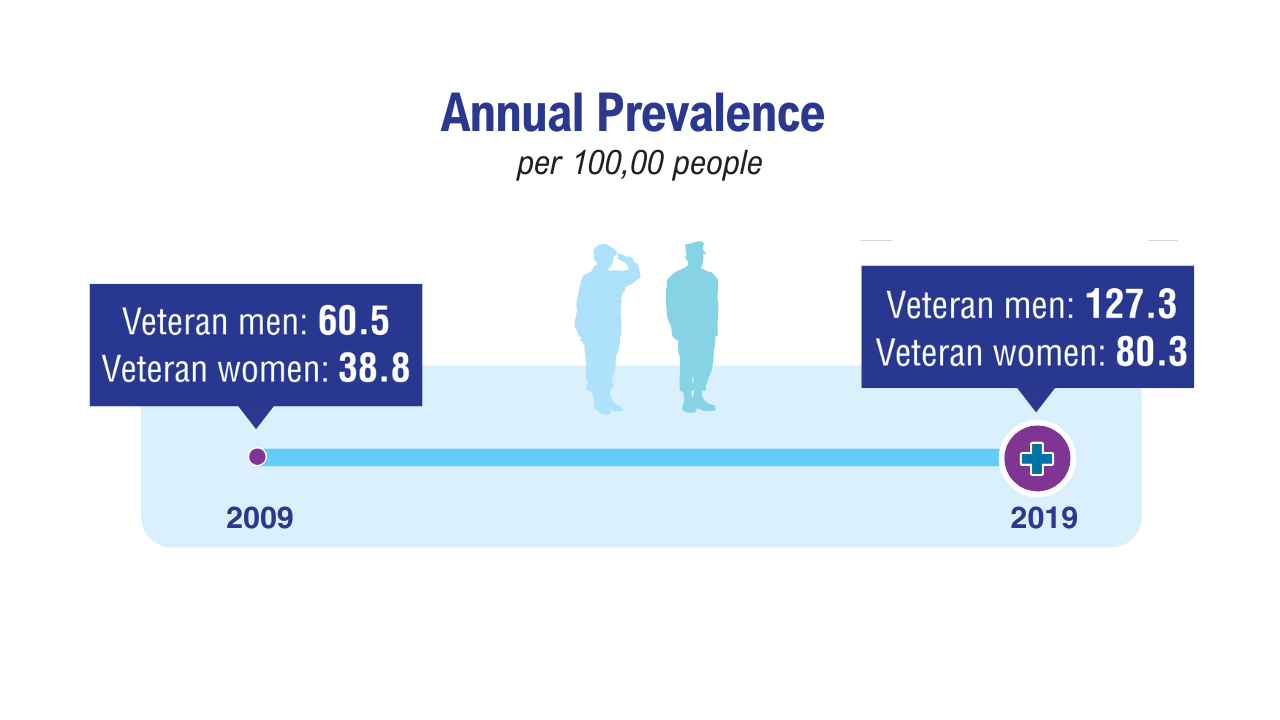 Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11
Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11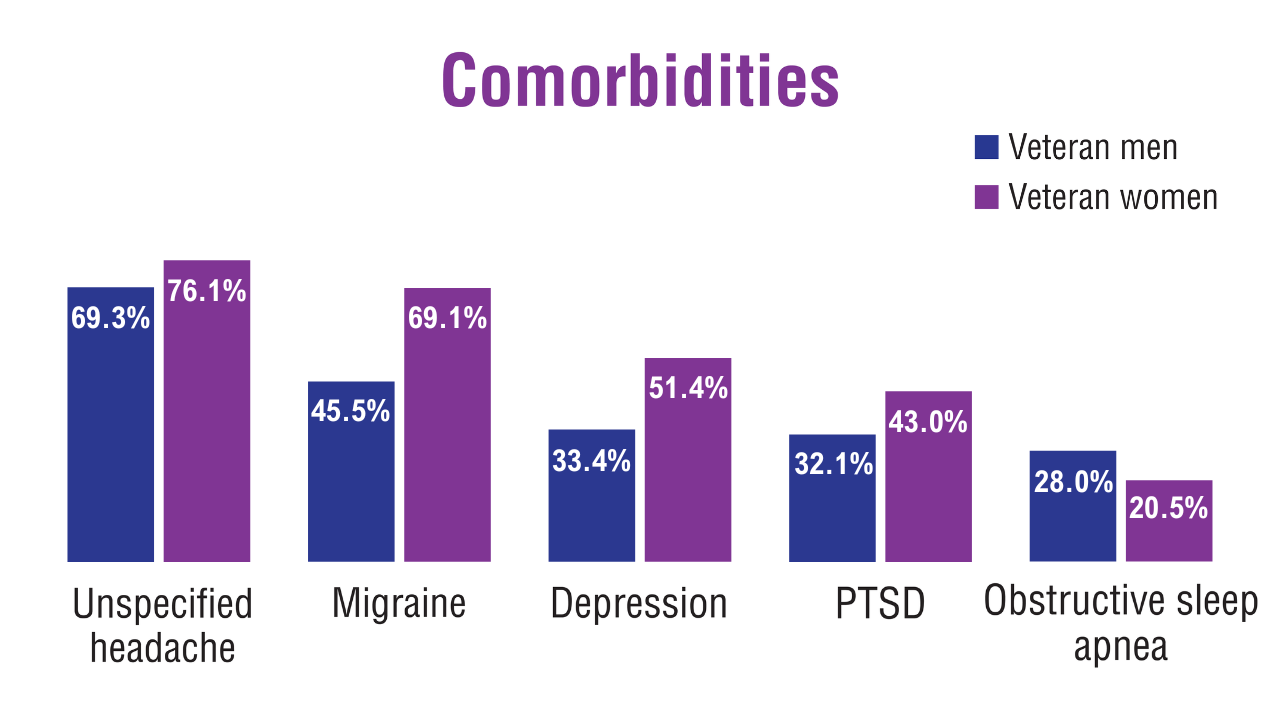 Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11
Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11 TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
The VA TBI Health Registry includes 441,639 veterans with TBI symptoms who sought care from September 2001 to September 2021. TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
This cohort represents 28.5% of all post-9/11 veterans who sought care at the VHA over a 2-decade period. TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
Veterans with TBI accounted for 11.0% of all inpatient care and 12.1% of all outpatient visits at the VHA. More than 108,000 veterans from this group submitted TBI-related disability claims. Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
A study of 491,604 veterans analyzed data from the Million Veteran Program to assess the prevalence of migraine and the effect of comorbidities and military service exposures Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
Veterans with migraine were younger (by 8.7 years on average), less likely to be married or cohabiting, and less likely to have a household income < $60,000 than veterans without migraine. Migraine was also associated with TBI, with an odds ratio of 4.82 in men and 2.92 in women. Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11
Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11 Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11
Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11 TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
The VA TBI Health Registry includes 441,639 veterans with TBI symptoms who sought care from September 2001 to September 2021. TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
This cohort represents 28.5% of all post-9/11 veterans who sought care at the VHA over a 2-decade period. TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
TBI in Post-9/11 Veterans10
Veterans with TBI accounted for 11.0% of all inpatient care and 12.1% of all outpatient visits at the VHA. More than 108,000 veterans from this group submitted TBI-related disability claims. Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
A study of 491,604 veterans analyzed data from the Million Veteran Program to assess the prevalence of migraine and the effect of comorbidities and military service exposures Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
Migraine Prevalence and Associated Factors in Veterans5
Veterans with migraine were younger (by 8.7 years on average), less likely to be married or cohabiting, and less likely to have a household income < $60,000 than veterans without migraine. Migraine was also associated with TBI, with an odds ratio of 4.82 in men and 2.92 in women. Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11
Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11 Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11
Gender Differences in Cluster Headache Comorbidities11
Click to view more from Federal Health Care Data Trends 2025.
,false