Painless Nodule on the Leg
The Diagnosis: Plasmablastic Lymphoma
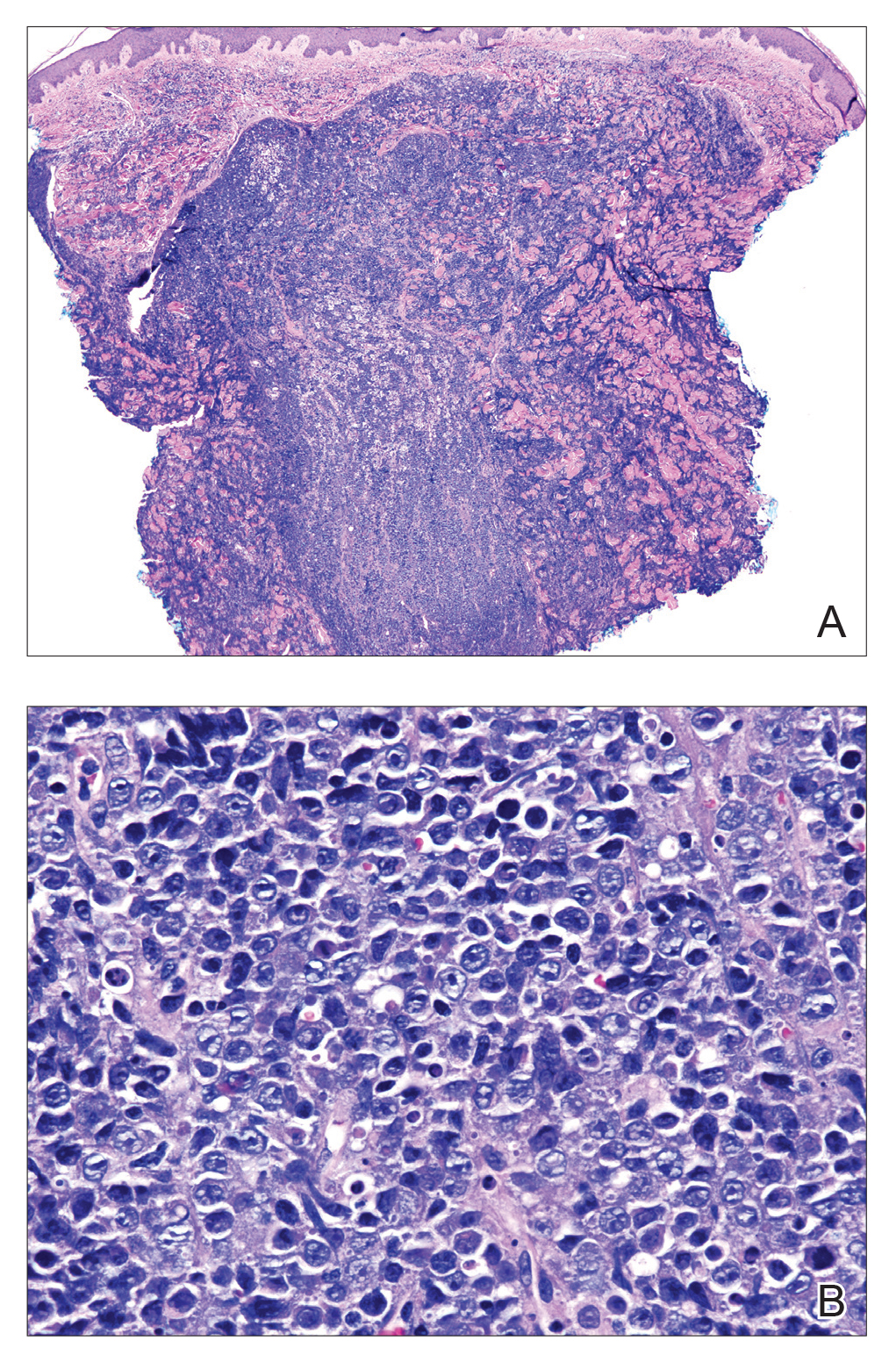
Histopathologic examination revealed a diffuse dense proliferation of large, atypical, and pleomorphic mononuclear cells with prominent nucleoli and many mitotic figures representing plasmacytoid cells in the dermis (Figure). Immunostaining was positive for MUM-1 (marker of late-stage plasma cells and activated T cells) and BCL-2 (antiapoptotic marker). Fluorescent polymerase chain reaction was positive for clonal IgH gene arrangement, and fluorescence in situ hybridization was positive for C-MYC rearrangement in 94% of cells. Epstein-Barr encoding region in situ hybridization also was positive. Rare cells stained positive for T-cell markers. CD20, BCL-6, and CD30 immunostains were negative, suggesting that these cells were not B or T cells, though terminally differentiated B cells also can lack these markers. Bone marrow biopsy showed a similar staining pattern to the skin with 10% atypical plasmacytoid cells. Computed tomography of the left leg showed an enlargement of the semimembranosus muscle with internal areas of high density and heterogeneous enhancement. The patient underwent decompression of the left peroneal nerve. Biopsy showed a staining pattern similar to the right skin nodule and bone marrow, consistent with lymphoma.
He was diagnosed with stage IV human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) and received 6 cycles of R-EPOCH (rituximab, etoposide phosphate, prednisone, vincristine sulfate, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride) without vincristine with intrathecal methotrexate, followed by 3 cycles of DHAP (dexamethasone, high dose Ara C, cisplatin) with bortezomib and daratumumab after relapse. Ultimately, he underwent autologous stem cell transplantation and was alive 13 months after diagnosis.
Plasmablastic lymphoma is a rare subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that most commonly arises in the oral cavity of individuals with HIV.1 In addition to HIV infection, PBL also is seen in patients with other causes of immunodeficiency such as iatrogenic immunosuppression following solid organ transplantation.1 The typical disease presentation is an expanding mass in the oral cavity; however, 34% (52/151) of reported cases arose at extraoral primary sites, with a minority of cases confined to cutaneous sites with no systemic involvement.2 Cutaneous PBL presentations may include flesh-colored or purple, grouped or solitary nodules; an erythematous infiltrated plaque; or purple-red ulcerated nodules. The lesions usually are asymptomatic and located on the arms and legs.3
,On histologic examination, PBL is characterized by a diffuse monomorphic lymphoid infiltrate that sometimes invades the surrounding soft tissue.4-6 The neoplastic cells have eccentric round nucleoli. Plasmablastic lymphoma characteristically displays a high proliferation index with many mitotic figures and signs of apoptosis.4-6 Definitive diagnosis requires immunohistochemical staining. Typical B-cell antigens (CD20) as well as CD45 are negative, while plasma cell markers such as CD38 are positive. Other B- and T-cell markers usually are negative.5,7 The pathogenesis of PBL is thought to be related to Epstein-Barr virus or human herpesvirus 8 infection. In a series of PBL cases, Epstein-Barr virus and human herpesvirus 8 was positive in 75% (97/129) and 17% (13/75) of tested cases, respectively.1
The prognosis for PBL is poor, with a median overall survival of 15 months and a 3-year survival rate of 25% in HIV-infected individuals.8 However, cutaneous PBL without systemic involvement has a considerably better prognosis, with only 1 of 12 cases resulting in death.2,3,9 Treatment of PBL depends on the extent of the disease. Cutaneous PBL can be treated with surgery and adjuvant radiation.3 Chemotherapy is required for patients with multiple lesions or systemic involvement. Current treatment regimens are similar to those used for other aggressive lymphomas such as CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone).1 Transplant recipients should have their immunosuppression reduced, and HIV-infected patients should have their highly active antiretroviral therapy regimens optimized. Patients presenting with PBL without HIV should be tested for HIV, as PBL has previously been reported to be the presenting manifestation of HIV infection.10
The differential diagnosis for a rapidly expanding, vascular-appearing, red mass on the legs in an immunosuppressed individual includes abscess, malignancy, Kaposi sarcoma, Sweet syndrome, and tertiary syphilis.
Acknowledgment
We thank Sameera Husain, MD (New York, New York), for her assistance with histopathologic photographs and interpretation.




